Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common condition that affects how your ovaries work. It can cause hormonal imbalances, irregular periods, excess hair growth, acne, weight gain, and insulin resistance. It can also make it harder for you to get pregnant.
PCOS is one of the most common causes of infertility in women. It affects 5–13 percent of women of reproductive age, according to Healthline. But having PCOS doesn't mean you can't have a baby. There are many treatments and strategies that can help you improve your fertility and achieve your pregnancy goals.
In this blog post, we'll explain how PCOS affects fertility, what are the symptoms and diagnosis of PCOS, what are the treatment options for PCOS-related infertility, and what are some lifestyle changes that can help you manage PCOS and boost your chances of getting pregnant.
How PCOS Affects Fertility
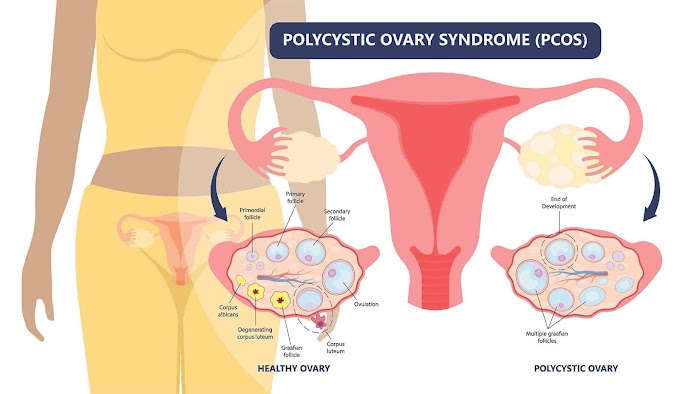
PCOS affects fertility by interfering with ovulation, which is the process of releasing an egg from your ovaries each month. If you don't ovulate regularly or at all, you may have fewer opportunities to conceive.
PCOS causes ovulation problems by disrupting the balance of hormones that regulate your menstrual cycle. These hormones include:
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which stimulates the growth of follicles (small sacs) in your ovaries that contain eggs.
- Luteinizing hormone (LH), which triggers the release of an egg from a mature follicle.
- Estrogen, which is produced by the follicles and prepares the lining of your uterus for pregnancy.
- Progesterone, which is produced by the corpus luteum (the remains of the follicle after ovulation) and maintains the lining of your uterus until your next period or pregnancy.
Women with PCOS often have high levels of androgens, which are male hormones such as testosterone. Androgens can inhibit the production and action of FSH and LH, leading to fewer or no mature follicles and eggs.
Women with PCOS may also have high levels of insulin, which is a hormone that helps your body use glucose (sugar) for energy. Insulin resistance means that your body doesn't respond well to insulin and produces more of it to try to lower your blood sugar levels. High insulin levels can also stimulate your ovaries to produce more androgens, further affecting your ovulation.
As a result of these hormonal imbalances, women with PCOS may experience:
- Irregular or absent periods
- Multiple small cysts in their ovaries (polycystic ovaries)
- Difficulty getting pregnant
- Increased risk of miscarriage
Symptoms and Diagnosis of PCOS
The symptoms of PCOS vary from person to person and may change over time. Some of the common signs and symptoms of PCOS are:
- Irregular or absent periods
- Excess hair growth on the face or body (hirsutism)
- Thinning hair on the scalp
- Oily skin or acne
- Weight gain or difficulty losing weight
- Insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes
- Mood changes or depression
- Sleep problems or sleep apnea
If you have any of these symptoms and suspect you may have PCOS, you should see your doctor for a diagnosis. There is no single test for PCOS, but your doctor may use a combination of methods to diagnose you, such as:
- Asking about your medical history, menstrual cycle, symptoms, and family history
- Doing a physical exam to check for signs of excess hair growth, acne, obesity, or other features of PCOS
- Doing blood tests to measure your hormone levels, blood sugar levels, cholesterol levels, and other markers of health
- Doing an ultrasound scan to look at your ovaries and check for cysts or other abnormalities
Your doctor may also rule out other conditions that can cause similar symptoms, such as thyroid disorders, adrenal disorders, or pituitary tumors.
Treatment Options for PCOS-Related Infertility
The treatment for PCOS-related infertility depends on your goals and preferences. Some women may want to try natural or alternative remedies first, while others may opt for medications or surgery. Your doctor can help you weigh the benefits and risks of each option and choose the best one for you.
Some of the treatment options for PCOS-related infertility are:
Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes are often the first step in treating PCOS-related infertility. Losing weight, eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, managing stress, and quitting smoking can all help improve your hormonal balance, ovulation frequency, insulin sensitivity, and overall health.
Research shows that losing as little as 5–10 percent of your body weight can restore ovulation and improve pregnancy rates among women with PCOS. A healthy diet that is low in refined carbohydrates and high in protein, fiber, healthy fats, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help lower your blood sugar levels and reduce inflammation. Exercise can help burn calories, improve blood flow, regulate hormones, and enhance mood. Stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, breathing exercises, or counseling can help reduce cortisol levels and promote relaxation.
Lifestyle changes can also help prevent or treat some of the complications associated with PCOS,
Cardiovascular disease, Diabetes,
Endometrial cancer,
and depression.

.jpg)


.png)
0 Comments